Earn Your D.O. at Maine’s Only Medical School
For more than 40 years, the University of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine (UNE COM) has created compassionate, community-minded physicians. As a student in our Osteopathic Medicine degree, you focus on whole-body health and learn to thrive in team environments to create the best possible patient outcomes.
UNE COM is Maine’s number one provider of physicians. Nationally recognized for leadership in primary care, rural medicine, osteopathic medicine, and geriatric healthcare, we are ranked among the country’s top medical schools.
Why UNE for your D.O.
Graduates of the UNE Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine are prepared for successful health careers, we rank in the top 10 for average score on the COMLEX-USA exam.
A UNE COM education happens within a supportive culture, in state-of-the-art facilities on beautiful Maine campuses. You experience an innovative curriculum at our high-fidelity simulation lab and learning laboratories for clinical skills, anatomy, and osteopathic manipulative medicine. Courses incorporate interprofessional education and are led by expert faculty who use small-group, team-based, and peer teaching.
What will you study? Osteopathic Medicine Curriculum Overview
About Osteopathic Medicine and the Profession
Osteopathic Medicine is a distinctly American branch of medicine that pioneered the concepts of wellness and the whole-person approach to health when it was developed in the late 1800s. Doctors of osteopathic (D.O.s) bring a philosophy that considers the mind-body-spirit connection to the evidence-based care of patients. Through the lens of wellness, D.O.s help patients with a full range of medical treatment options, including surgery, pharmaceuticals, and manual medicine. As a physician or surgeon practicing osteopathic medicine, you bring a unique patient-centered approach to the full spectrum of health care.
Becoming a D.O. requires four years of medical school after obtaining a bachelor’s degree. The first two years, pre-clerkship years, focus on building a foundation of biomedical and medical knowledge and skills. During the second two years, clerkship years, you apply and expand your knowledge and skills in clinical settings. The course of studies leading to the D.O. degree must be completed within 6 years of matriculation (or within 150% of the standard time to obtain the degree).
Learn more about osteopathic medicine
Pre-Clerkship and Clerkship
The pre-clerkship curriculum occurs on campus where the fundamental knowledge of anatomy, manual medicine, clinical skills, and medical sciences are taught primarily in small group, team-based, and simulation settings.
Clerkship training takes place at one of our clinical campuses throughout the Northeast. You spend time on various specialty services at clinics and hospitals, gaining firsthand experience providing medical care in different settings. During your fourth-year, you participate in the Match or one of the other post-graduate training assignment programs, which — depending on your specialty — take an additional three to seven years to complete.
Curriculum
| Program Required Courses | Credits |
|---|---|
| DOM 503 – Osteopathic Medical Knowledge IA | 14 |
| DOM 507 – Osteopathic Clinical Skills IA | 14 |
| DOM 510 – Osteopathic Medical Knowledge IB | 14 |
| DOM 511 – Osteopathic Clinical Skills IB | 14 |
| DOM 612 – Osteopathic Medical Knowledge IIA | 16 |
| DOM 616 – Osteopathic Clinical Skills IIA | 12 |
| DOM 618 – Osteopathic Medical Knowledge IIB | 16 |
| DOM 622 – Osteopathic Clinical Skills IIB | 12 |
| Total Credits | 112 |
| Program Required Clinical Clerkship Rotations | Weeks | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| FAMD 701 – Family Medicine Clerkship | Variable | Variable |
| IMED 701 – Internal Medicine Clerkship | Variable | Variable |
| OBGY 701 – Obstetrics/Gynecology Clerkship | Variable | Variable |
| PEDS 701 – Pediatrics Clerkship | Variable | Variable |
| PSCH 701 – Psychiatry Clerkship | Variable | Variable |
| SURG 701 – Surgery Clerkship | Variable | Variable |
| Total Weeks and Credits | 42 | 42 |
| Program Required Selective Clinical Rotations | Weeks | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| Selective Emergency Medicine Clinicals | 4 | 4 |
| Selective Internal Medicine Clinicals | 4 | 4 |
| Selective Osteopathic Medicine Clinicals | 4 | 4 |
| Selective Surgery Clinicals | 4 | 4 |
| Approved Elective Rotations (see below)* | 24 | 24 |
| Total Weeks and Credits | 40 | 40 |
| Minimum Total Required Credits | 194 |
|---|
*All Elective Rotations have a formal approval process.
Elective Rotations**
| Elective Rotation Disciplines | Weeks | Credits |
|---|---|---|
| Anesthesia | 2+ | 2+ |
| Community Health | 2+ | 2+ |
| Dermatology | 2+ | 2+ |
| Emergency Medicine | 2+ | 2+ |
| Internal Medicine | 2+ | 2+ |
| Military Medicine | 2+ | 2+ |
| Neuro TA | 2+ | 2+ |
| Neurology | 2+ | 2+ |
| Ob/Gyn | 2+ | 2+ |
| OMM | 2+ | 2+ |
| Pathology | 2+ | 2+ |
| Pediatrics | 2+ | 2+ |
| Psychiatry | 2+ | 2+ |
| Radiology | 2+ | 2+ |
| Research | 2+ | 2+ |
| Surgery | 2+ | 2+ |
**These are the common elective rotations taken. This is not a comprehensive list.
Courses
UNE’s integrated interdisciplinary curriculum is delivered over the first two (2) years through concurrent semester-long longitudinal courses titled Osteopathic Medical Knowledge (OMK) and Osteopathic Clinical Skills (OCS). The courses run in parallel within common clinical frameworks with frequent integration between the courses.
The student is required to complete eighty-two (82) weeks of clinical training in years three (3) and four (4) (typically forty-two (42) to forty-eight (48) weeks are done in the third year). UNE COM defines three (3) categories of clinical requirements:
Core — Forty-Two (42) Weeks
Required Discipline — The student is assigned by the UNE COM Department of Clinical Education; Core rotations are typically referred to as “clerkships.” The clerkship year schedule requires a rotation in Family Medicine, Pediatrics, OB-GYN, Psychiatry, and Surgery, and two (2) rotations in Internal Medicine.
Family Medicine
Core Family Medicine is a hospital and/or ambulatory experience that enhances the student’s understanding of patient and family dynamics in illness and health, the physician/patient relationship, and the careful and economical use of medical therapeutics, technological and laboratory investigation, and hospitalization. Special attention is given to the patient interview, directed physical examination, and patient education.
Internal Medicine
Core Internal Medicine is two (2) core rotations (general or mix of general plus subspecialty) and may complete one (1) or more additional rotations in Internal Medicine subspecialties, typically in a hospital setting. Applying principles learned in the preclinical years, and working within a multidisciplinary team, the student learns to formulate a differential diagnosis based on the history and physical, prioritize a problem list, identify appropriate diagnostic tests, develop a treatment plan, and present patients to supervising physicians and in team meetings. Further developing and refining the ability to communicate effectively with patients and members of the treatment team is of critical importance.
Obstetrics and Gynecology
Core Obstetrics and Gynecology is intended to provide practical clinical exposure in the diagnosis and management of the female patient with normal and pathologic obstetric and gynecologic processes. Gynecologic procedures, surgery, labor and delivery, fetal evaluation and monitoring, pre-operative evaluations, and post-operative care are emphasized.
Pediatrics
Core Pediatrics places an emphasis on primary care of the newborn to the adolescent. In hospital and/or ambulatory settings, the student gains a greater understanding of the continuum of child development, including physical, social, and emotional aspects, as well as the role of family dynamics. The student develops communication skills with both the pediatric patient and the family and, as appropriate, refines their skill at educating the child, parents, and other caregivers in health promotion.
Psychiatry
Core Psychiatry encourages the student to recognize, screen for, and assess key symptoms of common mental illnesses, using the mental status examination as the basis for differential diagnosis and therapy. Additional content areas include cognitive, psychomotor, and affective development, risk assessment, substance abuse issues, and the impact of mental illness on patients and families.
Surgery
Core General Surgery and one (1) selective in General Surgery or a surgical subspecialty must be completed by each student. This clerkship is an introduction to the principles and practice of surgery. The student will experience the totality of care from the patient’s pre-surgical visit through the surgical encounter and post-operative recovery.
Emergency Medicine
Emergency Medicine selective represents where knowledge and skills gained by the student in Core rotations come together in the fast-paced emergency department. In conjunction with emergency department personnel, the student will evaluate and treat patients of all ages who are experiencing medical, surgical, or psychiatric emergencies.
Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine
Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine focuses on osteopathic philosophy and principles, which are intrinsic to the entire curriculum and are incorporated throughout the clinical portion of the student’s education. In the fourth year, the student completes a total of four (4) weeks of osteopathic manipulative medicine to gain in-depth experience by working with a practitioner who is well versed in these principles and utilizes them in the clinical care environment.
Selective — Sixteen (16) Weeks
Required Discipline — Site selected by the student, subject to approval by the Department of Clinical Education. There are four (4) weeks each of Emergency Medicine, Internal Medicine, Surgery, and Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine.
Elective
Discipline and site selected by the student, subject to approval by the department.
Elective Rotation Requirements
Sufficient quantity to meet graduation requirements.
Graduation Requirements
The Board of Trustees of the University of New England confers the Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) degree upon those students who have satisfactorily completed the requirements for graduation and who have been recommended for graduation by the faculty of the College.
Every candidate for the degree of Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine must:
- Be of good moral character and meet the UNE COM standards for professional behavior and conduct as described under academic and technical standards.
- Have met and completed the academic requirements of the College, including passage of COMLEX-USA Level 1 and 2CE, within six (6) academic years (or within 150% of the standard time) for the awarding of the degree and have been enrolled at this college for at least the last two (2) years. Successful completion of or its equivalent is under discussion by the COCA and consideration of this graduation requirement will be adjusted based on their decision. Each student must pass the third-year clinical assessment examination provided by UNE COM.
- Be free of indebtedness to this College, the University, and their affiliates.
- Have demonstrated the ethical, personal, and professional qualities deemed necessary for the successful and continuing study and practice of osteopathic medicine.
- Have been recommended by the faculty for graduation.
- Be present at the University Commencement Ceremony as well as the UNE COM Physician Hooding Ceremony of their class at the time the degree is conferred, unless otherwise excused by the Dean.
An Alternative Approach to Clinical Rotations
UNE COM is one of fewer than 30% of medical schools to offer a Longitudinal Integrated Clerkship (LIC) — an alternative way of organizing the third-year clinical experience that is modeled after residency programs. Rather than rotating through six-week blocks focusing on a single discipline, you are embedded within a primary care clinic where you follow your own patients for the year while experiencing specialty-focused time on the days when you are not assigned to a clinic. The LIC applies the residency training model to third-year clerkships. As a student who participates in LICs, you:
- Earn equal or greater clinical skills and exam scores
- Build professional relationships with colleagues and patients
- Are placed at one of six host sites in Maine
A Care for the Underserved Scholars Program for Additional Skill Building
This two-year honors distinction program enables you to participate in clinical and non-clinical activities in a variety of rural and urban underserved settings. You will:
- Improve leadership skills
- Gain competencies in interprofessional education and team-based practice
- Understand and address health disparities and the social determinants of health in rural and underserved communities
- Understand the role of practice transformation in addressing significant health and public health issues
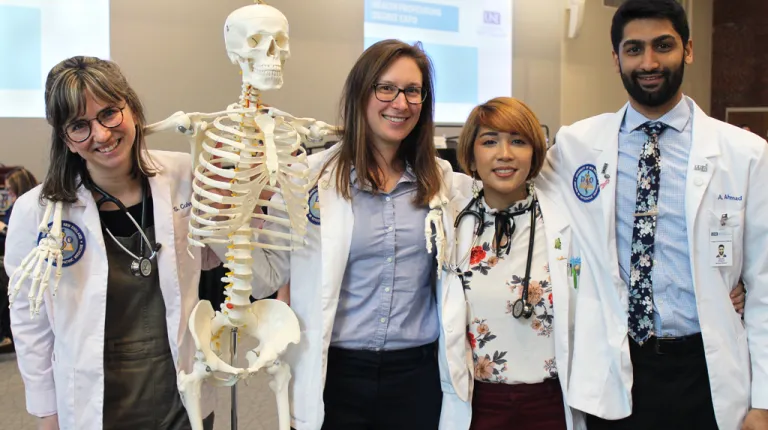
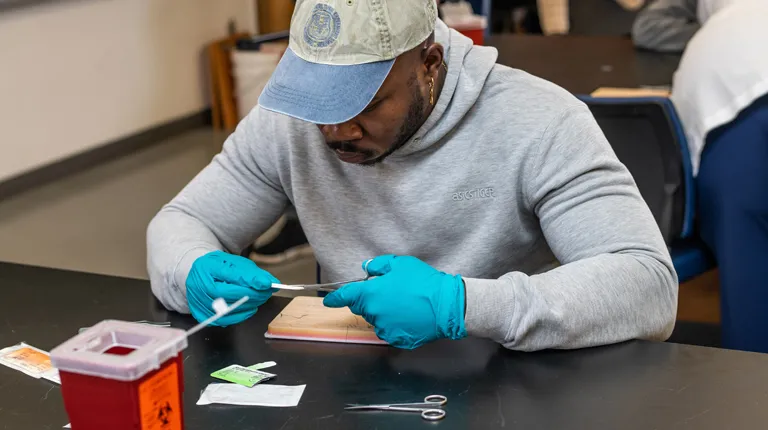




Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine Facilities
Harold and Bibby Alfond Center for Health Sciences
The Harold and Bibby Alfond Center for Health Sciences is a brand-new, four-story facility that serves as the home of UNE COM. It features a 240-seat tiered lecture hall, a health center with 20 fully equipped exam rooms for patient simulations, an Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine patient clinic, and a donor lab with 50 dissection tables — the only one of its kind in southern Maine.
Interprofessional Simulation and Innovation Center
As a D.O. student, you utilize our Interprofessional Simulation and Innovation Center to apply the knowledge that you gain in the classroom to realistic clinical situations before putting actual patients at risk.
Guided by skilled instructors, you participate in simulations specifically designed to enhance your clinical aptitudes. Rather than just hearing and reading about difficult or unusual cases, you experience them by treating high-fidelity patient simulators and patient actors in scenarios that mimic real life.
Portland Laboratory for Biotechnology and Health Sciences
The Portland Laboratory for Biotechnology and Health Sciences encompasses a 5,000-square-foot research space on the third floor and basement level of the UNE Pharmacy building on the Portland campus. The laboratory is equipped with instrumentation to support and enable research conducted by UNE faculty and students from across the University as well as external partner institutions.
This modern research space provides infrastructure for ongoing research in therapeutic discovery, biosensor development for biomanufacturing, translational pharmacology, biomarker development and drug metabolism/pharmacokinetic research. In addition to providing infrastructure for state-of-the-art research, a major focus of this laboratory is to provide workforce development opportunities for students with interest in careers in biotechnology and health sciences.
Pickus Center for Biomedical Research
The Pickus Center for Biomedical Research is a state-of-the-art biomedical research building that houses research teams of UNE faculty and students. The 22,000 sq. ft. structure includes six laboratories, enabling you to engage in important research as part of your curriculum.
Stella Maris Hall
Stella Maris Hall houses 12,000 sq. ft. of laboratory and office space on UNE’s Biddeford Campus. Neuroscience faculty share core facilities dedicated to behavioral phenotyping, electrophysiology, histology, and molecular biology. The building also contains an animal vivarium, BSL-2 level laboratories, and other labs that support a multidisciplinary approach to understanding brain function and diseases of the nervous system.
Osteopathic Medicine: Team Based Learning
Home to Maine’s only dental school and a full range of other health professions programs, UNE offers you the opportunity to learn from and interact with students and faculty from across health care disciplines. It’s a concept known as interprofessional education (IPE), and UNE is a national leader in this approach. With team-based care now the gold standard, our expertise in providing collaborative learning experiences gives our medical students a significant edge in the workforce and, more importantly, better patient outcomes.
In addition to the interprofessional experiences you’ll gain through curriculum and clinical rotations, you may pursue other IPE opportunities offered by three of our University partners: The Center for Excellence in Aging and Health (CEAH), the Center to Advance Interprofessional Education, and the Center for Excellence in Public Health. You’ll have the unique opportunity to use such experiences toward your Interprofessional Honors Distinction.
Research in the Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine program
We recognize and support the role of research in all of our educational, clinical, and basic science activities. Research is fundamental to excellence in teaching and the creation of a scholarly atmosphere for learning.
With eight centers of research and scholarship, UNE is designated as a “doctoral university with high research activity” by the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education. Six of these centers are health-related, and you’ll have the opportunity to collaborate with faculty in a wide array of research, including projects related to metabolic disease, immunology, neuroscience, pain management, aging, and more. You may also apply for funding to conduct original research through one of our student research fellowships. Additionally, the Northern Light Rural Scholars program spans years 1–3 and combines research experience with clinical training in a rural Maine setting.
Post-Doc Education
UNE’s commitment to the continuation of medical education extends beyond graduation. Both on campus and at affiliates throughout the Northeast and into the Mid-Atlantic, UNE COM partners with or sponsors residency programs that highlight our passion for osteopathic medicine and our dedication to training osteopathic physicians who serve the world. Learn more about Continuing Medical Education at UNE
Meet UNE D.O. Students
Living and Learning in Maine
As a student in one of our College of Osteopathic Medicine programs, you’ll study on UNE’s historic Portland Campus. Our Portland Campus for the Health Sciences is located in a quiet neighborhood that is a 10-minute drive from the downtown waterfront. The campus is close to major clinical sites as well as countless attractions and amenities. Named “America’s Most Livable City” by Forbes and “Foodiest Small Town in America” by Bon Appetit, Portland is the city on every list.
Take a Virtual Tour of Our Portland Campus
Who can apply to the doctor of osteopathic medicine degree program?
To apply to our D.O. degree program, you must have completed 90 semester hours or 75% credit progress towards a bachelor’s degree, to be earned at a U.S. regionally accredited college or university, or international equivalent. You must also hold a 2.8 cumulative GPA.
All applicants must apply through the American Association of Colleges of Osteopathic Medicine Application Service (AACOMAS).
Financial Aid at UNE
Finance your education through loans, grants, and scholarships. We are committed to making our osteopathic medicine degree program as affordable as possible.
Apply Today
Ready to begin your future in UNE’s D.O. program?

Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine FAQ
What is osteopathic medicine?
Osteopathic Medicine is a distinct American branch of evidence-based, mainstream medicine that stresses promoting health as much as reacting to disease. As a physician or surgeon practicing osteopathic medicine, you bring a unique patient-centered approach to the full spectrum of health care. Through the lens of wellness, Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.s) help patients with a full range of medical treatment options, including surgery, pharmaceuticals, and manual medicine.
Osteopathic medicine is a hands-on approach to diagnosis and treatment. In addition to the standard medical school curriculum, D.O.s receive extensive training in the neuromusculoskeletal system and osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT), a form of manual medicine treatment. Osteopathic principles and practices are a comprehensive approach to health care in which D.O.s apply the use of osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT) and an osteopathic philosophy during the diagnosis and management of patients.
Osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM) is a form of treatment taught to student doctors studying osteopathic medicine. OMM is a comprehensive approach to health care in which D.O.s apply the use of osteopathic manipulative treatment (OMT) and an osteopathic philosophy during the diagnosis and management of patients.
As a medical student at the University of New England’s College of Osteopathic Medicine in Portland, Maine, you will learn about OMM treatment techniques in addition to the standard medical education curriculum.
Currently 10% of physicians in the United States are graduates of osteopathic medical schools and bring a philosophy that considers the mind-body-spirit connection to the evidence-based care of their patients.
What is a doctor of osteopathic medicine (D.O.)?
Doctors of Osteopathic (D.O.) Medicine are physicians or medical specialists who know that health is interconnected with all aspects of a person’s life and are trained to see patient care as the synthesis of a philosophy focused on the interconnectedness of the whole person with a deep knowledge of anatomy and the basic sciences. As a D.O., you are trained in medical school to consider the big picture when treating patients. Osteopathy emphasizes the goal to support a patient’s overall health as well as address acute symptoms.
While in osteopathic medical school, student doctors receive specialized training in the musculoskeletal system and treatment. UNE’s medical school in Maine has the mission to advance exceptional osteopathic healthcare locally and globally through practice, research, scholarship, education, and community health. Through this mission, UNE D.O. students learn how to see the body as an integrated unit of systems that work together to heal and maintain health. Osteopathic medical doctors recognize that the whole body’s structure should be optimized to facilitate its ability to self-regulate.
What is the difference between an M.D. vs. D.O.?
Doctors of Medicine (M.D.) and Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine (D.O.) can practice in the same specialties and train in the same residency programs. The difference is the framework in which D.O.s approach patients and view healthcare. D.O.s are taught to recognize the importance of the mind-body-spirit connection to wellness. Osteopathic doctors look beyond symptoms to other factors which may impact a person’s health. The combination of a philosophy focused on wellness and rigorous training in science and medicine enables D.O.s to truly partner with their patients in the healthcare process.
Although D.O. and M.D. students receive similar curricular content in medical school, student doctors of osteopathic medicine receive that content through the lens of wellness and the mind-body connection. D.O. students also receive specialized training in the diagnosis and treatment of the neuromusculoskeletal system using osteopathic manipulative medicine (OMM). Since D.O.s are trained to see the body as an integrated unit of systems that work together to heal and maintain health, they recognize that the whole body’s structure should be optimized to facilitate its ability to self-regulate.
Physical examination and palpation are more heavily emphasized in the D.O. curriculum. On average, UNE medical students and other D.O. schools spend more time practicing hands-on physical examination skills than M.D. students. D.O. students also learn OMM treatment options to address pain and other issues.
Both D.O. and M.D. schools have the same level of rigor and length of schooling: generally two years of classroom training followed by two years of clinical training. Upon graduating with your medical degree, both Doctors of Osteopathic Medicine and Doctors of Medicine will go on to specialty training in residency and fellowships in the same programs.
What are medical school requirements?
Medical school applicants should demonstrate the motivation, discipline, and altruism to pursue a career as a physician. This includes successful completion of a comprehensive undergraduate education and appropriate experiences that can be translated to the medical profession.
Every medical school has slightly different requirements. It’s a good idea to review the admissions requirements of the specific medical school program that interests you. If you are applying to an M.D. program, most schools require you to apply through the American Medical College Application Service (AMCAS). If you are applying to a D.O. program, most schools require you to apply through the American Association of Colleges of Osteopathic Medicine (AACOMAS).
The University of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine (UNE COM) in Maine participates in the AACOMAS centralized application service. All applicants are required to apply online through this service. At UNE COM, it’s required that you have completed 90 semester hours or 75% credit progress towards a bachelor’s degree, to be earned at a U.S. regionally accredited college or university, or international equivalent, at the time of application.
Although not required, it is helpful to have done some study in the biological sciences, physical sciences, social sciences, or other health sciences. At UNE COM, there are some prerequisite coursework requirements that should be reviewed during your application.
During your medical school application process, many schools will also require you to submit your GPA. As calculated by AACOMAS, the minimum cumulative GPA is 2.8 at the time of application. Additionally, the completion of the Medical College Admissions Test (MCAT) is required. Although UNE’s medical school does not have a minimum score requirement, highly competitive applicants typically score in the 50th percentile or higher on the MCAT.
You should also expect to be required to submit letters of recommendation, complete a personal statement, and take part in an interview process while applying for medical school. At UNE’s osteopathic medical school, applications for admission are reviewed holistically by the UNE COM Committee on Admissions based on fit for the Mission, Vision, and Core Values of UNE COM and a combination of GPA, academic record, MCAT scores, applicant interview, and lived experiences.
What is the best osteopathic medical school for me?
When applying to medical school, you should look for one that fosters a state of wellness, equity, inclusion, and diversity across its community. If you are motivated to promote health by considering the big picture, then you should consider applying to an osteopathic medical school.
As a student at the University of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine in Portland, Maine, you will acquire a deep understanding of human anatomy and become an excellent practitioner of both traditional medical specialties and osteopathic manipulative medicine. As with most medical curricula, UNE COM students spend two years on campus, and two years training in clinical settings. The third year is spent at one of UNE COM’s clinical clerkship sites and fourth-year students are allowed to pursue experiences where they hope to do their residency. Clinical training during the last two years of medical school at UNE COM is typically completed at various affiliate hospitals and healthcare facilities across the northeast United States.
UNE COM students are part of a close-knit community with convenient access to urban opportunities that includes state-of-the-art facilities for medical research, anatomical study, manual medicine, and the development of foundational clinical skills.
As an osteopathic medical student, you will want to be surrounded by a supportive community of faculty, staff, and peers. At UNE COM, we pride ourselves on being student-centered, student-friendly, and family-friendly. D.O. students at UNE have countless opportunities both in and out of the classroom. Whether you participate in one of our more than 40 clubs and organizations or take part in research, your medical education will be supported at UNE.
Applying to a medical school that has an integrated interprofessional curriculum helps student doctors gain the skills needed to successfully collaborate with other healthcare professionals when entering the workplace. At UNE College of Osteopathic Medicine, you will learn in an environment that encourages collaborative practice to improve health outcomes of patients. UNE pursues a health-focused mission that includes programs in medicine, dental medicine, nursing, pharmacy, and an array of allied health professions, so UNE students benefit from an interprofessional health education.
How much do D.O.s generally make?
Salaries for D.O.s vary widely based on type of practice, practice setting, years of experience, and where you live. The average annual salary for doctors of osteopathic medicine is equal to or greater than $208,000 per year depending upon the specialty practiced.
D.O. graduates from the University of New England College of New England College of Osteopathic Medicine match to residency programs all over the country. UNE ranks in the top 10 for medical schools where graduates are mostly likely to match with their first choice residency program.
There is a high demand for D.O.s in every state, and Maine itself has a high concentration of job opportunities for physicians in a variety of practice settings. UNE is the number one provider of physicians for Maine.


